There’s a lot of talk about serverless computing lately, especially with the big tech giants investing in the idea and offering exclusive products built on it. But is it just a buzzword, or does it have the potential to become the next big thing in technology?
Cloud computing was once a buzzword, too, one may argue. But that buzzword ended up revolutionizing the whole industry, with 90 percent of companies now using cloud hosting. Serverless is the next step in that movement, one that’s poised to grow exponentially over the next few years. A survey by Cloud Foundry Foundation of 250 companies showed 22 percent of them were using serverless technology.
What is Serverless?
Serverless or, as it’s technically called, serverless computing is an execution model of cloud-based computing where the cloud provider dynamically assigns resources and storage. It basically runs pieces of code as functions rather than whole applications. And the client is charged only for the actual resources used.

In simpler words, serverless computing doesn’t involve provisioning and maintenance of servers (hence the term serverless). However, servers are still involved, of course. But developers are not responsible for provisioning. Instead, the provider manages the server end of things.
This model is also called function as a service (FaaS) because, essentially, the provider is only executing individual codes as functions. It’s more event-based, as only as many resources are allocated as required by that function.
Serverless architecture can process individual functions or interconnected functions creating a pipeline. The physical servers, virtual servers, and containers for running these functions are all managed by the cloud provider.
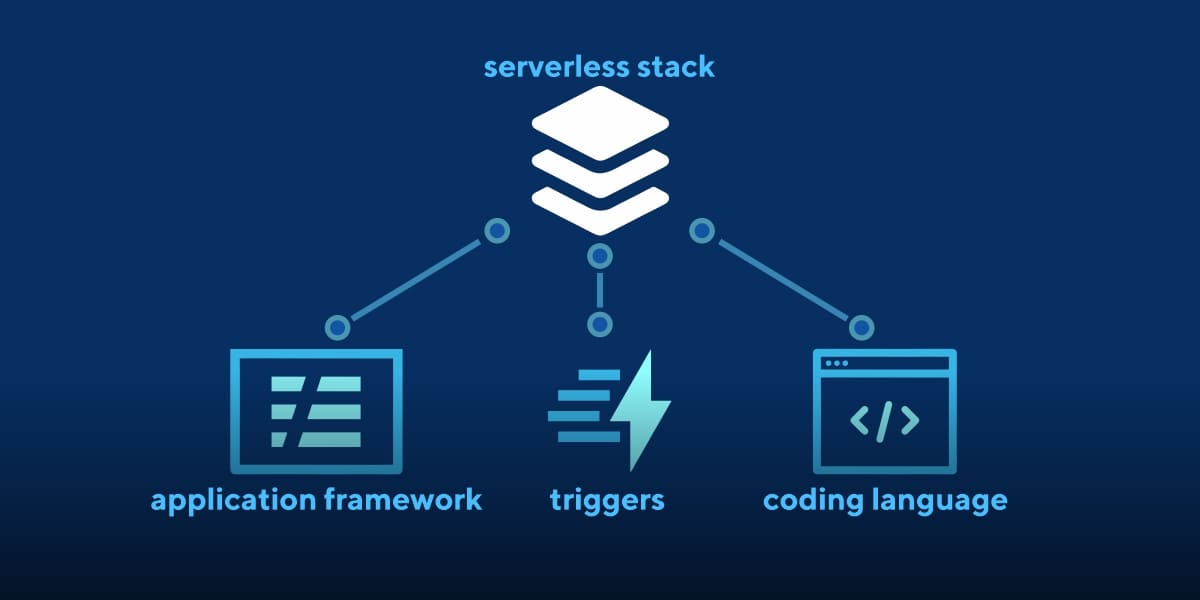
This technology has given rise to the concept of a serverless stack. Stacks represent different components of the serverless application, which includes application framework, coding language, and triggers. The triggers help the platform run serverless functions. It’s important to note that stacks may differ by platforms. Some platforms use specific programming languages exclusively, so you’re bound you can only use those for your applications.
Serverless Computing Benefits
Serverless computing is enticing some of the biggest companies around the world for two main benefits.
Business-Oriented Development
In a traditional application development setting, developers create code for the applications based on the business logic behind it. That application then needs to be deployed on servers, which, in a typical organization, is the responsibility of the infrastructure team. This distribution often creates problems and delays operations.
The time it takes the infrastructure teams to provision the servers for scaled applications creates delays for developers. It’s even more impactful for a small business as their developers are also dealing with all the back-end processes related to servers.
Serverless architecture swiftly resolves this problem, resulting in more productivity for the developers. They can focus on business logic and purely develop solutions without worrying about scaling up or down provisions, ensuring uptime, or applying security updates.
Granular Billing
The most significant advantage that’s driving the shift toward serverless is its pay-as-you-use nature. You literally pay for what you use. Typically, companies have to buy fixed resources at flat rates to accommodate peak requests/traffic, whenever that may be. This means that all the other times, those resources are not really being used, which makes this model not so cost-effective.
In serverless architecture, resources are dynamically assigned whenever requested. So it inherently has a granular approach to billing those resources. For instance, you have an application that only gets event requests at certain times of the day, and it’s slow or idle the rest of the time. Dynamic provisioning can ensure there’s no downtime and requests are handled properly, regardless of the volume.
With big companies spending millions on traditional servers and cloud-based architecture, serverless computing provides a way to control costs. It’s all the more beneficial for startups, as they are more often than not pressed for money in the initial phases.
Drawbacks of Serverless
Serverless technology is still in its early stages, which means it hasn’t been perfected yet. The biggest drawback is that it doesn’t offer the flexibility of easy migration. There are several major players in this nascent field, with each having a slightly different setup and framework. So you’re locked with the vendor you choose.
It can also be challenging to incorporate those codes on other platforms, as well as in-house. Therefore, this is something serverless providers have to work on to provide their clients the freedom to move whenever they want to. Then you have the issue of cold start, which is basically latency of an on-demand structure. However, this drawback is not that major since the latency can be as low as some microseconds.
Serverless Providers
Another sign that serverless isn’t just a buzzword is that major companies are providing this framework. The top vendors of serverless providers are:
- AWS Lambda
- Azure Functions
- Google Cloud Functions
- IBM Cloud Functions
The AWS serverless is the leading provider with the majority market share. They also have the most elegant and sophisticated solution, which major Fortune 500 companies are using AWS Lambda.

There are open-source frameworks available as well. The most popular of these open-source pilots is Serverless.com. You can use it to deploy applications on AWS and other platforms. So there’s room for more vendors to join the list.
As discussed above, you have to consider the serverless stack from the provider you choose. For instance, Google Cloud Functions involves triggers that are simple HTML requests. On the other hand, AWS has its own set of triggers.
Wrap Up
Serverless technology is making leaps by the second, and it’s estimated that this market would grow considerably in the near future. Cost-effectiveness for organizations and agility for developers is what is making this computing so desirable. AWS serverless is leading the movement for now, but other players are also making strides.
It would be interesting to see how it affects infrastructure monitoring and management. After all, monitoring is all about optimizing performance, reducing costs, and preventing attacks, all of which are at the core of serverless computing.




Leave a Reply